Table of Contents
Computer security systems such as modems have become more important since hackers began breaking into big computer systems illegally. To reduce these threats as well as attacks on the systems, sophisticated computer security solutions had to be developed by experts. Similarly, the first line of defense against such vulnerabilities is the awareness of computer security.
This blog explains every bit of relevant information about computer security. Let’s examine its definition, significance as well as all the threats and vulnerabilities it may prevent.
Computer security is the safeguard for computer systems to prevent unauthorized access, theft, or misuse of sensitive data. In the same way, intricate security techniques and procedures protect critical information, system access, and authorization. The hardware is secured in the same manner that sensitive equipment, such as lockers and doors, is secured.
Computer Security Relevance

Before an issue arises, there should be a computer security system installation or it may result in significant problems and concerns, at which point it will be too late to address them.
It is crucial to protect all types of information from unscrupulous hackers and stop important data from slipping away into the wrong hands for misuse, especially in a data-driven environment. Computer security protects sensitive data and also keeps a computer running smoothly without engaging in any disruptive activities.
Computer Security Types
1. Network Security
Network security consists of anything done to safeguard the usability and integrity of a network. In order to stop unwanted access to computer networks and systems it consists of particularly both hardware and software innovations.
2. Internet Security
One of the most crucial sorts of computer security comes with a collection of guidelines and procedures. It concentrates on certain dangers and activities that take place online. Internet security offers defense against malware, computer viruses, and DoS attacks but also hacking.
3. Endpoint Security
Eventually, end users are quickly turning into the biggest security risk. Hackers and attackers can enter an organization’s virtual gates with a lack of awareness at the user’s end. Since the majority of the end users are unaware of the ICT policy, users who often handle sensitive information must comprehend and learn about all complete security rules, protocols, and procedures.
4. Software Security
While the software is still under development, software security adds security components. This actively guards against potential online dangers including data breaches, DoS attacks, SQL injection, and many more. Web application firewalls as well as encryption, antivirus software, firewalls, etc. are a few types of software security tools.
5. Information Security
Information security is a set of procedures that protects the CIA triad—confidentiality, integrity, and availability—of data from unwanted access and usage. It is a set of security policies and techniques designed to protect sensitive company information against abuse, unauthorized access, interruption, or destruction also known as InfoSec. It generally includes physical and environmental security, access control, and cybersecurity.
Computer Security Attacks
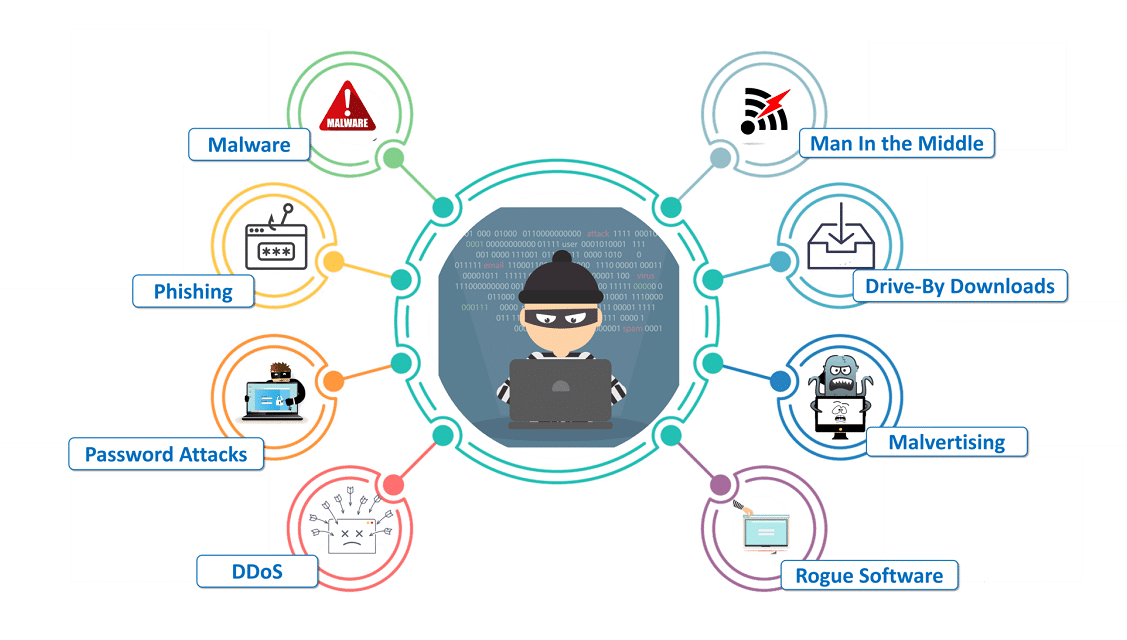
Threats to computer security are possible dangers that could prevent computers from operating normally. With the world becoming more digital, cyber risks are increasing daily. Let us examine the various serious risks to computer security, its problems, and at last its vulnerabilities.
1. Viruses
A dangerous application secretly placed onto a computer without the user’s knowledge is called a computer virus. This application can reproduce itself and spread the infection to all the system’s software and hence data files. In the worst-case scenario, these infections render the victim’s PC utterly inoperable.
2. DDoS
A distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack is an attack on system resources, but it is launched from a large number of other host machines infected with malicious software controlled by the attacker. In contrast to assaults that are meant to allow the attacker to gain or enhance access, denial-of-service attacks do not deliver direct benefits to the attacker. One common example of DDoS is Session Hijacking.
3. Drive-by download
Drive-by download attack is a common method of spreading malware. Hackers look for insecure websites and plant a malicious script into HTTP or PHP code on one of the pages. Accordingly, this script might install malware directly onto the computer of someone who visits the site, or it might re-direct the victim to a site controlled by hackers. Drive-by downloads can happen when visiting a website or viewing an email message or a pop-up window. To protect yourself from drive-by attacks, you need to keep your browsers and operating systems up to date and also avoid websites that might contain malicious codes. The more plug-ins you have, the more vulnerabilities there are that can be exploited by drive-by attacks.
4. Password Attack
Passwords are the most commonly used mechanism to authenticate users to an information system, obtaining passwords is a common but also effective attack approach. Access to a person’s password can be obtained by looking around the person’s desk, ‘‘sniffing’’ the connection to the network to acquire unencrypted passwords, using social engineering, gaining access to a password database, or outright guessing. The last approach can be done in either a random or systematic manner.
5. Malware
Malware is a general term for malicious software, hence the “mal” at the start of the word. It infects a computer and alters its functionality, destroys data, or eavesdrops on the user or network communication as it passes through. Malware can either spread from one device to another or stay in place, affecting only the host device. It can be used in several attack methods such as MITM attacks, phishing, ransomware, SQL injection, Trojan horses, drive-by attacks, and XSS assaults. It also requires the installation of software on the target device. As a result, this necessitates the user to take action. In addition to employing malware-detection firewalls, users should be informed which type of software to avoid, which links to verify before clicking, and which emails and attachments to avoid.
2. Keylogger
A keylogger is a type of spyware that not only track but also record all keystrokes. It can secretly follow as well as record all keyboard inputs and user activity. A keystroke logger is one of the typical methods for stealing someone’s login information. Keyloggers can also allow fraudsters to listen in on your conversations, view you through your system camera, or listen through your smartphone’s microphone.
3. Computer Worm
A computer worm is a piece of software that can reproduce itself from one computer system to another without the user’s knowledge. Due to their propensity to quickly replicate and consume up all available hard disc space, computer worms can severely deplete the system’s resources. Additionally, they can add new harmful applications to the system and edit or destroy files. Computer worms can also steal data and open a backdoor that allows hackers to access the system without authorization and take over.
4. Phishing
Phishing is a type of cybercrime that includes impersonating a legitimate organization over the phone, email, or text message in order to convince potential targets to divulge sensitive information like passwords or banking information. For example, financial losses and identity theft are the results of this. Although most people are cautious of these attacks, even though the majority of individuals are suspicious of such attempts, phishing is sadly very simple to fall for.
5. Rootkit
A rootkit is malicious software that intentionally hides its presence while being designed to grant unauthorized access to a computer or restricted regions. At this point, hackers can remotely execute files on the host computer and alter system settings through a rootkit. Rootkits allow hackers to steal personal data, and financial information, install malware or utilize computers as part of a botnet to send spam and participate in DDoS (distributed denial of service) attacks once they get unauthorized access to computers.
6. Botnet
A botnet is a network of linked computers that have been infiltrated by hackers against the users’ knowledge. Hence, each infected machine on the network is described by a term called “zombie computer”. In larger-scale operations such as DDoS, the infected computer which is now the bot is utilized to carry out nefarious acts.
Computer Security Best Practices

- Ensure the physical security of your devices and never leave your computer or smartphone bare in public. Otherwise, it would be a total invitation for it to be stolen.
- Run routine scans as well as frequently create system backups.
- Avoid pop-ups and drive-by downloads when browsing the Internet.
- Moreover, become knowledgeable about computer security fundamentals and the most recent online threats.
- Ensure that your company’s Wi-Fi network is safe. Also, it must be encrypted and concealed from others. You can use your company’s virtual private network if you work from home.
- Combat the system because attacks on computer systems and networks are becoming worse every day.
- Install security and antivirus software. Turn on the firewall and also update your programs and keep up with new updates.
- Avoid clicking on email attachments from anonymous senders, use secured passwords, and change them frequently.
- Be cautious while downloading or running apps. Download and use only those applications that are well-known and trustworthy. Obviously, get your downloads from the official websites.
- There are numerous additional ways to protect your computer system in addition to the ones mentioned above, such as computer cleaners and encryption.
Computer Security Career

The scope of a career in computer security is flourishing rapidly and offers a broad panorama of promising job options as computer security experts are in high demand. According to the research conducted by the cybersecurity professional association (ISC)2, there are around 3.1 million open vacancies globally.
Working in computer security also allows you to work in a fast-paced setting where you can always learn and progress. If you are working in the IT field or want to switch your career then computer security is something to consider about. Some of the best computer security career options are shown below.
1. Penetration Tester
As a defense against prospective threats and attacks, Penetration Testers seek to get into a network or computer system with permission to identify vulnerabilities, application problems, incorrect setups, and more. As a result, highly competent individuals and penetration testers frequently use tools created by them to break into secure systems.
The average salary is Rs. 303,000 (acc. to Glassdoor).
2. Computer Forensics Analyst
As part of their work with law enforcement authorities, forensic analysts combat cybercrime. They execute the task of recovering deleted files, following data trails, interpreting information related to crimes, or analyzing phone records.
The average annual salary is Rs. 377,136 (acc. to Glassdoor).
3. System Security Administrator
Installation, administration, maintenance, and troubleshooting of data and computer and network system security are all parts of the job of a System Security Administrator. They oversee everyday security system operations such as system monitoring, providing consistent backups, and managing individual user accounts.
The average annual salary is Rs. 498,879 (acc. to PayScale).
4. Ethical Hacker
Employers permit ethical hackers, who must hold a CEH certification, to attempt to breach their guarded systems. These methods aid in the evaluation of current security protocols and the creation of enhancements.
The average annual salary is Rs. 544,000 (acc. to Glassdoor).
5. IT Security Consultant
IT Security Consultants give clients advice on the most efficient and effective ways to secure their systems. Smaller businesses and government organizations with restricted budgets as well as occasional large corporations employ them to support their internal security team through outside viewpoint on system difficulties.
The average annual salary is Rs. 571,000 (acc. to Glassdoor).
6. Information Security Analyst
Consider Information Security Analysts as the first line of network protection. They are in charge of installing firewalls and encryptions to prevent security lapses, as well as continuously checking and auditing systems for irregularities.
The average annual salary is Rs. 573,000 (acc. to Glassdoor).
7. Cybersecurity Consultant
These cybersecurity specialists examine risks, threats, and problems before developing strong security plans for businesses. Cybersecurity Consultants offer firm advice on protecting their physical assets and data. These security assessments witness a wide range of criteria to consider.
The average annual salary is Rs. 815,000 (acc. to Glassdoor).
8. Software Security Developer
Securely building software and incorporating security into the applications are the responsibilities of software developers. Their responsibilities could include creating software security plans, managing a team creating security tools, taking part in the lifecycle of software development, and testing for vulnerabilities.
The average annual salary is Rs. 1,439,000 (acc. to Glassdoor).
9. Chief Information Security Officer
A company’s IT security section is led by a chief information security officer or CISO. They coordinate and plan all requirements for computer, network and data security. They establish an organization’s requirements for cybersecurity. CISOs are also in charge of hiring a team of security specialists, thus they need to have a solid foundation in HR, communication, and IT security architecture and strategy.
The average annual salary is Rs. 1,742,000 (acc. to Glassdoor).
10. Security Architect
Security Architects build a network and computer security programs to implement them for an organization. They design intricate security frameworks and guarantee their effectiveness. Their task is to create security systems that can eradicate all viruses, DDoS, and hacker attacks.
The average annual salary is Rs. 1,903,000 (acc. to Glassdoor).
Conclusion
Computer security programs continuously develop new defences against these new risks and discover new ways to battle them as a result of the dynamic nature of security threats. The majority of computer security risks are largely preventable, and most other security issues can be resolved by maintaining computer systems secure. With the right combination of AI-driven solutions and user awareness, organizations can significantly improve their computer security posture.
Also check,
Register in Henry Harvin to become a certified & skilled Cyber Security professional. Hone your Endpoint and Date Security, Cloud Security, and Application Security skills in just one platform. Henry Harvin offers best Certified Cyber Security Professional Course. It ranks no. 1 among the top 5 by BW Education.
FAQs
Cyber World is a virtual environment made up of interconnected computer systems and networks, where all computers are connected and may speak with each other. The phrase first appeared in science fiction in the 1980s, and it rose to prominence in the 1990s.
At the moment, the Ministry of Home Affairs has established a centralized website for the online filing of complaints on cybercrime throughout India. For crime related to women, children or any other cybercrime, report to:
http://www.cybercrime.gov.in/
If you like constant job challenges, and skill development then Computer Security is the right field for you. In India, there is a severe need for Computer Security professionals across all businesses, guaranteeing employment in numerous sectors.
First make sure that you choose science as your 10+2 major with physics, chemistry, and mathematics as your basic subjects, with a computer science or biotechnology specialization as an option. Before an M.Tech in Cyber Security, B.Tech in Cyber Security from a reputed college in India can be pursued. These credentials could pave the way for an exciting career in cyber security.
You need a broad range of specialized technological abilities if you want to have a successful career in cyber security. Your abilities must include cloud security, malware analysis and reversing, programming, hacker-like thinking, risk analysis and risk reduction, security analysis, and intrusion detection.



.webp)
