Table of Contents

“In this world, nothing can be said to be certain, except death and tax.“
BY BENJAMIN FRANKLIN.
As a tax specialist, I have come up with the top 30 tax interview questions, along with descriptive and concise answers for each of the tax interview questions. It’s a great information source to refer to for understanding the subject of Tax, as a referral source to be used. Especially for students for attending entrance examinations and interviews on TAX-related subjects. So, this source of Tax interview questions is indeed a great mode to start your preparation and to enhance your subject on Tax. The role of a tax specialist in this regard of outlining Tax interview questions along with answers is to better reach and solve the queries of readers on Tax. OK readers, I hope it helps u to further your knowledge of Tax
1. What is tax and why is tax levied and collected?
Income Tax Specialist Certification Course
45-min online masterclass with skill certification on completion
$99 FREE
Access Expires in 24Hrs
Upcoming Batches of Income Tax Specialist Certification Course :-
| Batch | Mode | Price | To Enrol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starts Every Week | Live Virtual Classroom | 12500 | ENROLL NOW |
Ans: A tax specialist describes the tax as a financial charge/levy imposed by the government. The word is derived from the Latin word ‘tax is’ meaning to estimate. It’s levied by the government to carry out public expenditures to solely realize the goal of social welfare.
It is not voluntary payment by a taxpayer, but it’s a mandatory obligatory and mandatory contribution to be made by an individual or any organization.
Concerning India, our Constitution through laws enforces the government to levy and collect taxes to meet its developmental goals. It can be in the form of taxes, charges, fees, or cess.
Since India has a federal setup of governance, both central and state governments are authorized to levy by Schedule 7. It outlines the central and state lists to carry out its fulfillment.to know about the Income Tax course Visit Here
2. What is taxation?
Ans: Taxation is the process of imposing or levying taxes by the government or taxable authority on individuals and business entities. It ranges from income tax to goods and services tax (GST), taxation applying to all levels. The accounting and Taxation course is available at Henry Harvin,
The government through progressive policy reforms has brought changes in taxation. To streamline the process of taxation, and ensure transparency, efficiency, and digitization of the whole taxation system, several innovative changes have been adopted within the system at almost all levels. One of the recent ones is the introduction of GST, which eased the tax regime in the sales and supply of goods and services, it brought a comprehensive indirect system in the country.
3. What are constitutional provisions for taxation related to GST?
Ans: https://cleartax.in/s/gst-law-goods-and-services-tax#comp
4. What are direct and indirect taxes?
Ans: The tax system is classified into broad categories such as:
- Direct
- Indirect
Direct is directly levied over the person or the property and companies and corporations over their profits. A responsible legal entity will pay directly to the government. Some direct taxes are as follows:
- tax-includes salary and other sources of income.
- Corporate tax-over business entities.
- Wealth tax over the property holdings.
- Estate duty paid in case of inheritance.
- Gift tax
- Fringe Benefits Paid by an employer for its employees over the fringe benefits provided.
Indirect is to be collected from the third person. of the cases, the consumers have to pay for goods and services, and manufacturers transfer over the retailers and the dealers.
Recent tax reforms have overhauled the taxation system in India, bringing the ‘ONE NATION, ONE TAX’ regime i.e.; the Goods and Services Act (GST) since 2017. It came into effect on July 1st, 2017. Since then taxation has been studied and understood concerning GST.
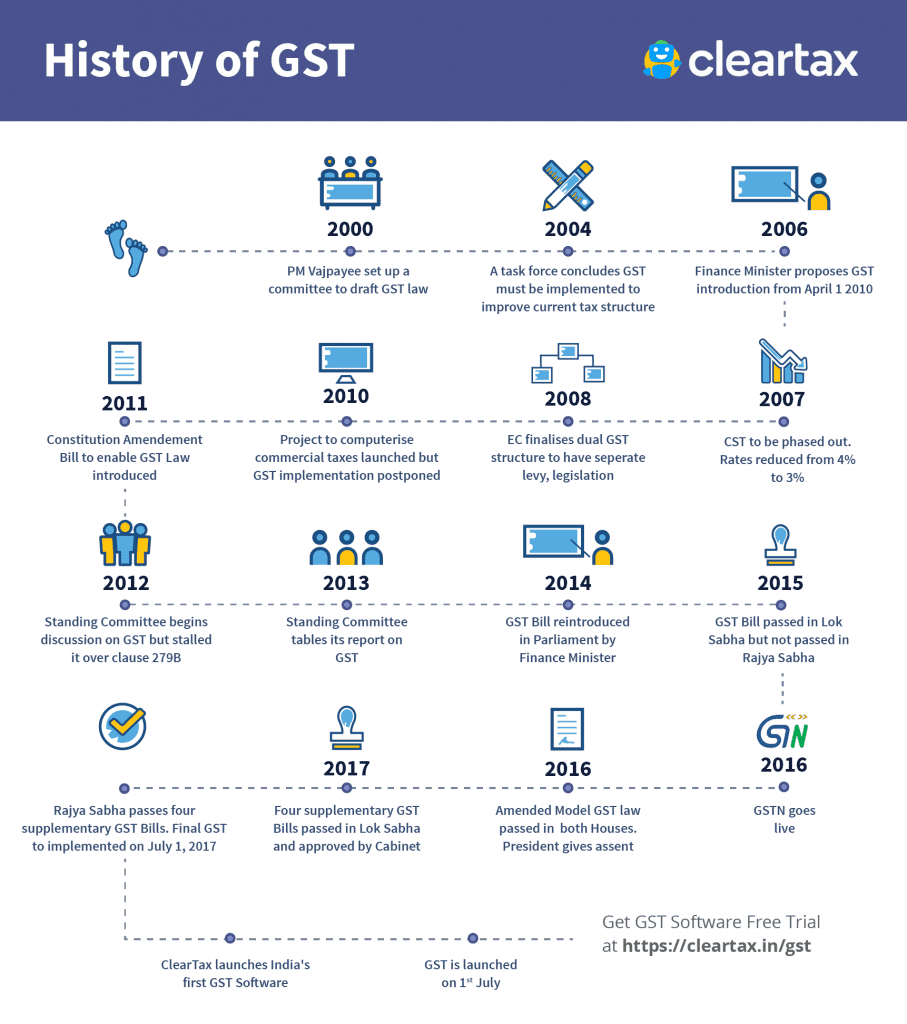
5. Briefly explain the history of the tax regime in India.
Ans: since British rule for 1st time was introduced in 1860 as explained through a chart:

Indirect Tax Reform Timeline Reference: (SKILLS for GST course)
- 1974 Report of LK Jha Committee suggested VAT
- 1986 Introduction of a restricted VAT called MODVAT
- 1991 Report of the Chelliah Committee recommends VAT/GST and recommendations accepted by Government
- 1994 Introduction of Service Tax
- 1999 Formation of Empowered Committee on State VAT
- 2000 Implementation of uniform floor Sales tax rates Abolition of tax-related incentives granted by States
- 2003 VAT implemented in Haryana in April 2003
- 2004 Significant progress towards CENVAT
- 2005-06 VAT implemented in 26 more states
- 2007 First GST stuffy was released By Mr. P. Shome in January
- 2007 F.M. Announces for GST in Budgetary Control Speech
- 2007 CST phase-out starts in April 2007
- 2007 Joint Working Group formed and report submitted
- 2008 EC finalizes the view on GST structure in April 2008
6. What is GST?
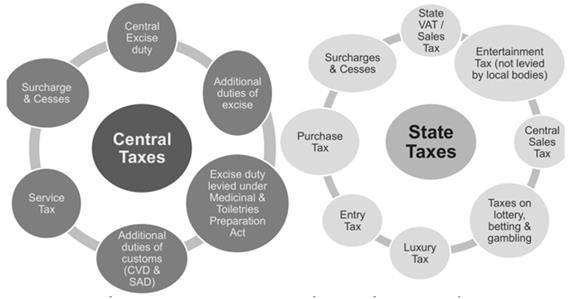
Ans: The Goods and Services Act (GST) is a single indirect system over the nation. It is a comprehensive system that encapsulates the various indirect taxes being charged by the government.It aims to have one Uniform tax rate at different slabs across the territory. It is levied on both goods and services. It revolutionizes our tax structure, realizing the goal of the act i.e. One Nation, One tax system.GST course is also available online
It is levied by both central and state governments in this federal governance with different slabs applicable to goods and services with exemptions.
GST compromises the following:
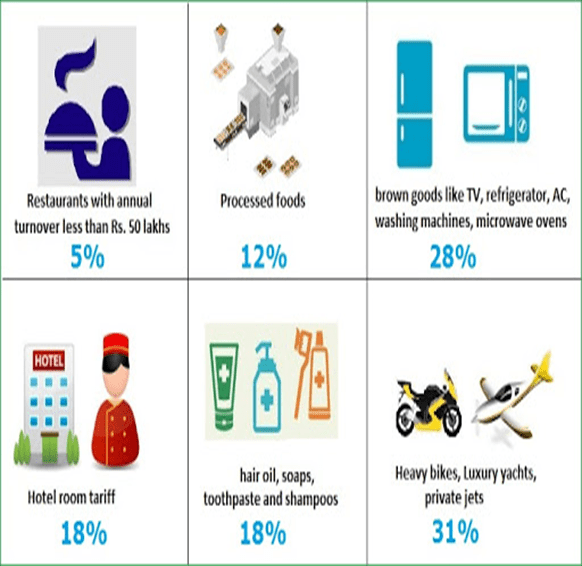
Different slabs for Goods and Services:

7. What are the salient features of the GST?
Ans: some of the features are as follows:
- It is a value-added tax, applied to the value addition at every stage, starting from
- Manufacturer to the dealer to distributor to the final consumer, giving way to the cascading effect.
- It is destination and supply-based.
- It is levied by both central and state governments by laws such as
- Central good and Services Act (within the state)
- State Goods and Services Act(within the state)
- Integrated Goods and Services Act(interstate
- It aims to avoid the multiplicity of tax rates and widen the base throughout the country.
8. Define income tax.
Ans: It is a direct tax levied on every taxable individual at different tax rates depending upon their income within their jurisdictions. The taxable person has to file the returns annually to meet his/her tax obligations. The income of every person is calculated at different heads as:
- Salary
- All wages, dividends, interests, etc.
- Rental income
- Income from property
| TAX SLAB | PERCENTAGE |
| 5 lacs-7.5lacs | 10% |
| 7.5lacs-10lacs | 15% |
| 10lacs-12.5lacs | 20% |
| 12.5lacs -25lacs | 28% |
Periodically assessed and applied based on Income tax slab rate as shown below in the table:
Check out our Income Tax Online Course for a better understanding of the concepts.
9. A brief introduction of GST through a video?
Ans: https://www.vskills.in/lms/topic/what-is-gst-5/
10. Explain some of the important GST terms.
Ans: Accounting and Taxation courses that carry on any business within the territory of India and are eligible to be registered under the GST Act.
Aggregate Turnover: The taxable turnover which includes taxable supplies excluding inward supplies on which reverse charge is applied.
Appellate Tribunal: It’s a GST tribunal.
Assessment: Self-assessment, reassessment, pro-assessment, summary assessment.
Capital Goods: List of capital assets mentioned in the Book of Accounts Book.
e-Commerce operator: who carries out business over digital or electronic mode.
Input Tax Credit: Credit claimed over the input taxable supplies.
Principal: On whose behalf does the agent carry out the business?
GST council: The highest decision-making and governing council body.
Supply: The taxable event in goods and services or both is the supply. It is defined based on parameters, such as below:
- Supply of goods or services
- Supply did for consideration
- Supply has been done for the furtherance of business
- Made by a taxable person
- It has to be a taxable supply
11. What is the GST Council?
Ans: The Goods and Services Tax Council(GSTC) is the constitutional body governing the implementation of the GST Act throughout the country. It is constituted under Article 279A of the constitution, which is under the One Hundred and one (101st) Act,2016 to be constituted by the president, by order, within 60 days to form a council called GSTC.
It is headed by the honorable Union Finance Minister and comprises the state finance ministers including two Union territories of Delhi and Puducherry. It’s a joint forum and the highest decision-making body for the implementation of the GST Act.
- It is entrusted with the following Mandated, as outlined below:
- It recommends both central and state governments’ issues related to goods and services.
- It looks into the principles that govern the supply of goods and services.
- It determines the threshold limit of the turnover
- It determines the GST slab rates.
- It determines the special charges for the special category states of
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Jammu n Kashmir
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Sikkim
- Tripura
- Himachal Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
It can also establish the mechanism to adjudicate the cases arising from the GST issued between the states and between the center and the states.
Its importance is at every level of the implementation of the Act.
12. What is GST registration?
Ans: It is a process for every taxable person to get registered under the act and get a GSTIN number. A person, having a business entity whose turnover exceeds Rs.40lakhs(Rs.10Lakhs in the case of special category states) is required to get registered.
Under the act, the following categories have been identified to get it registered and as follows:
- Individuals registered under Pre-GST
- Business entities whose turnover exceeds Rs.40lakhs.
- Casual taxable person/Non-Resident Taxable person
- Agents of Supplier and Input service distributor.
- Those payable under the Reverse Charge Mechanism
- E-Commerce
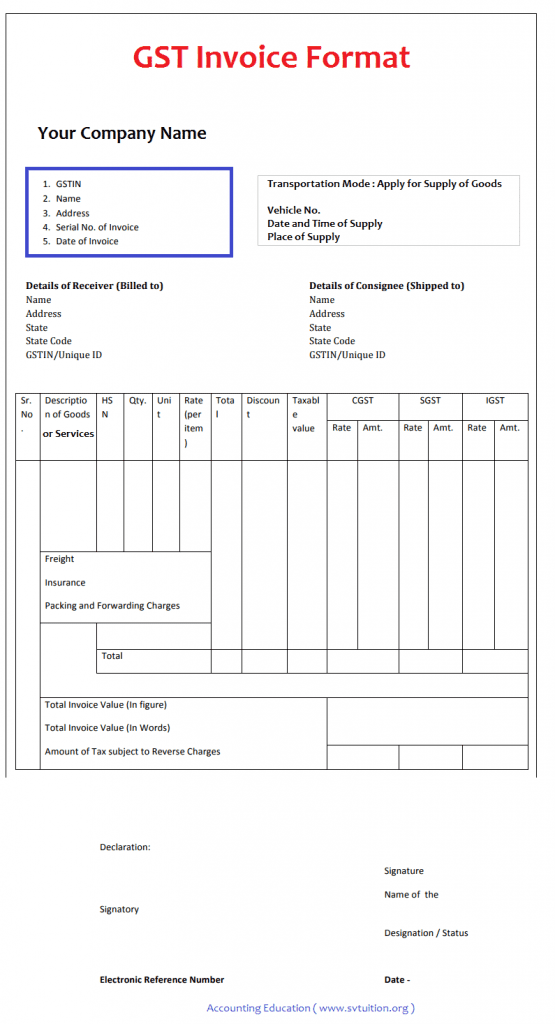
13. What is Tax Invoice?
Ans: The ‘tax invoice’ or ‘invoice’ is referred to under section 31 of the CGST Act,2016. It is an important and legal entity that mandates the registered person to issue a tax invoice for the supply of the goods and the services made. If supply is done by an unregistered person, then the recipient has to issue a Bill of supply instead of a tax invoice.
It is an important means to avail of Input Tax Credit made by the supplier. Also, it is important evidence for the supply made. The GST is charged at the time of supply of goods and services, so the tax invoice is the indicator for the supply made.
It compromises the name of the supplier and the recipient. the amount due for the payment, description of the goods made, quantity, and value, and other details are outlined.
In the case of the person dealing with exempted goods and maybe availing the Composition Scheme is eligible to issue a Bill of Supply instead of the invoice.
The invoice format is shown below:
14. What is Composition Scheme?
Ans: It is to be availed by small traders having a turnover of less than Rs.1.5cr and wanting to escape themselves from the tedious formalities of paying Gst at a fixed rate of turnover.
The turnover of all the businesses registered under the same PAN number is to be considered.
Exemptions:
- Manufacturer of icecreams, pan masala, and tobacco
- Interstate supplier
- Casual Taxable person/NRTP
- e-Commerce operators
Conditions to be considered under CS:
- He cannot claim the ITC claimed.
- He cannot supply the exempted goods
- He has to mention as composition Taxable Person over his signboard in his shops.
- Several businesses undertaken by him to be collectively considered under a single PAN or opt out of the scheme
To register under the composition scheme, so to get login into the GST portal by filling out the form CMP 02.
Different rates for composition scheme dealers:
| Manufacturers and Traders | 1.0% |
| Restaurants not serving Alcohol | 2.5% |
| Other service providers | 3.0% |
15. What is the e-way bill?
Ans. It is an electron waybill to be generated on the ewaybillgst.gov.in bill portal. It is an important document to be carried by the transporter supplying the goods. It is to be generated for transporting goods whose value exceeds more than Rs.50,000.It can be generated by the supplier or the recipient in case of an unregistered person who does the supply or the transporter can also generate if not generated.
It simplified the process of transportation of goods, especially in the case of interstate supply. It has the details of the consignee and consigner, the address of the delivery place, the value of the goods, and of course the destined delivery date.
16. What is the time, place, and value of the supply of goods?
Ans: The supply includes all forms
Sales
Transfers
Barter
Exchange
License
Rental and also the Disposal or agreed to be made by the person for consideration under the furtherance of business.
The time of the supply is important to be considered. It is the time on which the charging event has occurred on that specific time the tax liability arises for the registered person to levy taxes or to avail the input tax credits he made during the furtherance of the businesses.
The supply can be considered at both forward and reverse charges. The table below shows for forward charges under the supply of goods and services.
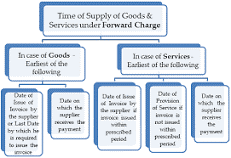
17. What are GST returns?
Ans: It’s a document to be filled by the taxable person in that financial year to file before the tax authorities, which includes
- Purchases
- Sales
- Output GST (On sales)
- Input tax credit (GST paid on purchases)
The GST is the destination-based. It simplified the indirect tax structure making it more efficient, and effective, and digitalized the whole tax structure. It has brought a friendly environment and a corruption-free regime throughout the country.
At the international trade forum, it has brought India to the forefront and placed it at better competitive terms.
It widened the tax base by bringing more comprehensive uniformity in our taxation system. It simplified the regime bringing the very need for GST and to be implemented as early as possible.
The tax is levied and collected to serve the purpose of welfare in financing public expenditures. The GST has brought further assurance of the expansion of the sources and brought out the model of a progressive tax system.
Since it is a One Nation, One Tax system, this federal structure of governance, has brought out cooperation and coordination in the tax system governance. This is a welcome development for overall economic growth and sustainable development of the country.
Still, the challenges of tax evasion and avoidance are a matter of concern. In the coming years, the compliance tax rate needs to further extend through stringent measures and laws. Also, the concerned authorities and official members of the tax system have to be well-equipped with the provisions of the act. Along with these progressive steps, awareness programs of the GST tax system are to be brought in at all the levels of the 3-tier structure of governance. That is even the local government has to be well versed with the need and importance of timely filing of tax returns.
In the coming years, it will continue its successive path. Let everyone pledge to pay our annual tax returns and to oblige our responsibilities. This Indirect tax system GST regime has put our country in a better position at the international trade forum.
Therefore its applicability is to be enforced in the coming days.
So readers, what u think of this GST system? Go through your respective state tax regime and visit your nearby office.
Recommended Reads:-
- Top 10 Business Accounting and Taxation (BAT) Courses Online
- Top 10 Business Accounting And Taxation (BAT) Courses In Delhi
- Top Accounting Interview Questions with Answers
- Top 10 Business Accounting and Taxation (BAT) Courses in Mumbai
- Top 10 Business Accounting And Taxation Courses in Bangalore
- Top 10 Business Accounting and Taxation (BAT) Courses in Chennai
- Top 10 Best Business Accounting and Taxation (BAT) Courses in India
FAQ’s
Q1- To become an income tax specialist which degree is best?
Ans- The candidate should have a bachelor’s degree in any specialisation field to become an income tax specialist. However, having basic knowledge of tax and finance can help the candidate.
Q2- What is an Income Tax Specialist Course?
Ans- An income tax specialist course is structured in a way so that you get a deep knowledge and become an expert in tax laws and regulations and interview preparations. Mostly syllabus covers the topics like different aspects of income tax, including filing procedures, deductions, credits, and compliance with tax laws.
Q3- What Skills Can I Gain?
Ans- Students acquire skills in tax preparation, analysing financial data, interpreting tax laws, attention to detail, and effective communication to assist clients in tax-related matters.
Q4- What Are the Career Opportunities?
Ans- After finishing the Tax specialist course you can apply for the posts like tax preparer, tax consultant, auditor, financial analyst, or even start your own tax consultancy business.
Q5- How much a Tax specialist can earn?
Ans- A tax specialist can earn an average income of ₹7,90,000 per year in India. Additionally, they also earn by getting cash compensation of around 90,000/-.
Q6- Can I Specialize in a Specific Area of Taxation?
Ans- Yes, many courses offer elective modules or advanced studies in specialized areas like corporate taxation, estate planning, international tax laws, or specific industry-related taxation.
Recommended Programs
Income Tax Specialist Course
by Henry Harvin®
100% Practical Income Tax Course| India's Best Certified Income Tax Course | Henry Harvin® Featured by Aaj Tak, Hindustan Times | Income Tax Course Training By Award-Winning Speakers | 2,665+ Income Tax Professionals Trained | Interactive Instructor-led Classes.
Accounting and Taxation Course
With Training
The Certified Accounting and Taxation Course (CATP) covers critical components of Accounting like GST, Income Tax, and TDS which have a crucial bearing on the modalities of Financial business operations in India. The CATP course is earmarked for professionals keen on building a successful career in Accounting and Taxation.
Best Advanced Excel Training &
Certification Online
No. 1 Ranked Advanced Excel Course in India | Trained 5,935+ Participants | Get Exposure to 11+ projects | Learn to Apply Advanced Formulas, Perform Data Analysis & Data Visualization, and Create Pivot Tables & Dashboards| Live Online Classroom Core and Brush-up Training Sessions
Tally Prime Course Course
Get Practitioner Certification
Tally Prime, the latest Tally Software used in Accounting, Taxation Software, Accounts Receivables, Accounts Payable, Inventory, Billing, and Payroll | Use Tally Prime to Calculate TDS, Income Tax, and GST | Earn a Rewarding Certification of Certified Tally Accountant (CTA), from Henry Harvin, the Award Winning Institute
Explore Popular CategoryRecommended videos for you
Tally ERP 9 Course Tutorial For Beginners
Post Graduate Program Income Tax by Henry Harvin®
Ranks Amongst Top #5 Upskilling Courses of all time in 2021 by India Today
View Course









.webp)
